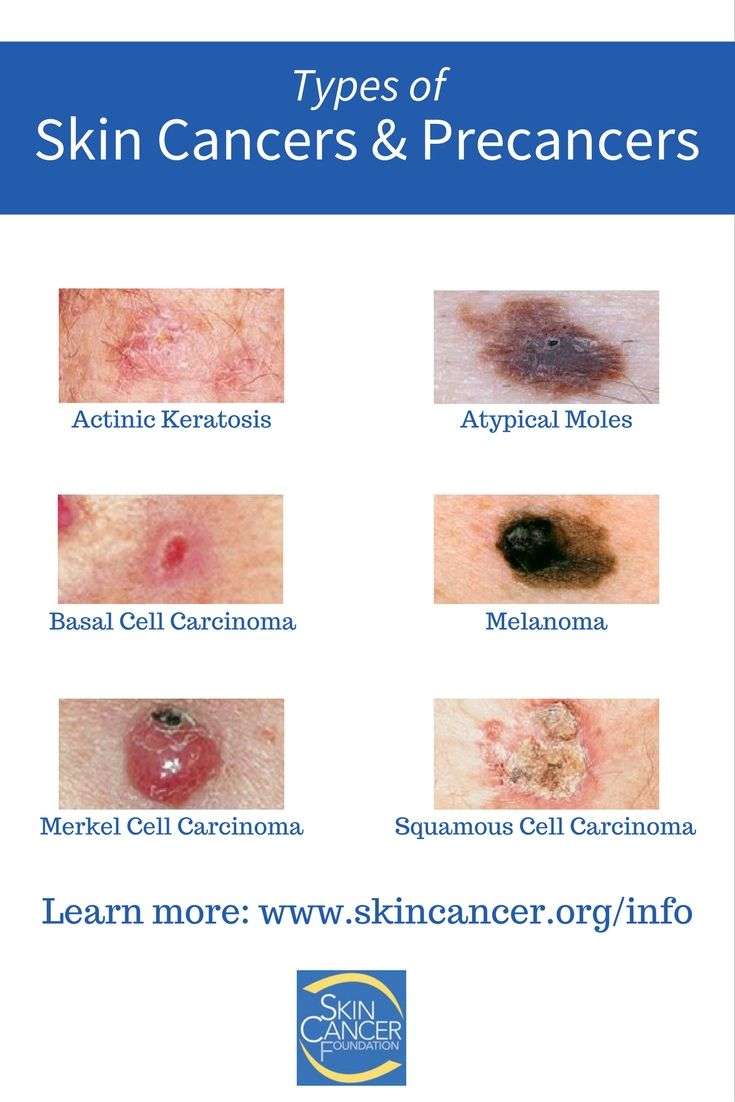
What Are The Four Main Types Of Melanoma Of The Skin
Superficial spreading melanoma
What you should know: This is the most common form of melanoma.
How and where it grows: It can arise in an existing mole or appear as a new lesion. When it begins in a mole that is already on the skin, it tends to grow on the surface of the skin for some time before penetrating more deeply. While it can be found nearly anywhere on the body, it is most likely to appear on the torso in men, the legs in women and the upper back in both.
What it looks like: It may appear as a flat or slightly raised and discolored, asymmetrical patch with uneven borders. Colors include shades of tan, brown, black, red/pink, blue or white. It can also lack pigment and appear as a pink or skin-tone lesion .
Lentigo maligna
What you should know: This form of melanoma often develops in older people. When this cancer becomes invasive or spreads beyond the original site, the disease is known as lentigo maligna melanoma.
How and where it grows: This form of melanoma is similar to the superficial spreading type, growing close to the skin surface at first. The tumor typically arises on sun-damaged skin on the face, ears, arms or upper torso.
What it looks like: It may look like a flat or slightly raised, blotchy patch with uneven borders. Color is usually blue-black, but can vary from tan to brown or dark brown.
Acral lentiginous melanoma
What you should know: This is the most common form of melanoma found in people of color, including individuals of African ancestry.
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form.
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: These are the cells that can become melanoma. They normally make a brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin protects the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
The Abcdes Of Melanoma
To help people find a possible melanoma on their skin, dermatologists created the ABCDEs of melanoma:
| A is for Asymmetry |
If you find a spot on your skin that has any of the ABCDEs of melanoma, see a board-certified dermatologist for a skin exam.
The following pictures can help you see how the ABCDEs of melanoma can appear on the skin.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Mammary Carcinoma Survival Rate
Skin Cancer Facts: How Common Is Melanoma Skin Cancer In The World
Melanoma is often used synonymously with the term skin cancer and the vast majority of melanoma cases do involve the skin.
However, in medical terms, it is defined as cancer that originates from melanocytes which are pigmented cells. This means that melanoma can also appear in the gut, nails, and eyes
Across Europe, Melanoma of the skin was the seventh most common cause of new cancer in 2018, whereas, across the world, melanoma was the 20th most common new cancer diagnosis.
It is possible that variations in UV light exposure, our daily activity patterns, and working lives may explain why there are differences in the rates of melanoma globally.
Rates of melanoma are highest in more developed regions , and it is possible that better awareness of the condition in a sophisticated health care system leads to more patients seeking advice on a concerning skin mark and subsequent diagnosis.
What Causes Skin Cancer
Almost all skin cancers in Australia are caused by too much exposure to UV radiation. This is the part of sunlight that causes tanning, sunburn and skin damage over time. UV radiation also comes from non-natural sources such as sun beds .
While anyone can get skin cancer, it is more common if you are older. The risk is also higher if you have:
- previously had skin cancer or have family history of skin cancer
- fair or freckled skin, particularly if it burns easily or doesnt tan
- red or fair hair and light-coloured eyes
- a weakened immune system
- sunspots or irregular moles on your body
- worked, played sport or spent leisure time in the sun
- actively tan or use sun beds
If you have olive or dark skin, your skin produces more melanin, which protects against UV radiation. However, its still possible for you to develop skin cancer.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
When Should I Call My Doctor
You should have a skin examination by a doctor if you have any of the following:
- A personal history of skin cancer or atypical moles .
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A history of intense sun exposure as a young person and painful or blistering sunburns.
- New or numerous large moles.
- A mole that changes in size, color or shape.
- Any mole that itches, bleeds or is tender.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a diagnosis of melanoma can be scary. Watch your skin and moles for any changes and seeing your doctor regularly for skin examinations, especially if youre fair-skinned, will give you the best chances for catching melanoma early when its most treatable.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2021.
References
Benign Tumors That Develop From Other Types Of Skin Cells
- Seborrheic keratoses: tan, brown, or black raised spots with a waxy texture
- Hemangiomas: benign blood vessel growths, often called strawberry spots
- Lipomas: soft growths made up of fat cells
- Warts: rough-surfaced growths caused by some types of human papilloma virus
Most of these tumors rarely, if ever, turn into cancers. There are many other kinds of benign skin tumors, but most are not very common.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Surgery For Skin Cancer
Small skin cancer lesions may be removed through a variety of techniques, including simple excision , electrodesiccation and curettage , and cryosurgery .
Larger tumors, lesions in high-risk locations, recurrent tumors, and lesions in cosmetically sensitive areas are removed by a technique called Mohs micrographic surgery. For this technique, the surgeon carefully removes tissue, layer by layer, until cancer-free tissue is reached.
Malignant melanoma is treated more aggressively than just surgical removal. To ensure the complete removal of this dangerous malignancy, 1-2 cm of normal-appearing skin surrounding the tumor is also removed. Depending on the thickness of the melanoma, neighboring lymph nodes may also be removed and tested for cancer. The sentinel lymph node biopsy method uses a mildly radioactive substance to identify which lymph nodes are most likely to be affected.
Continued
Melanoma Skin Cancer Rates By Country
- In 2018, there were over 140,000 new cases of melanoma of the skin across Europe
- Over the next twenty years, by the year 2040, it is predicted that the incidence of new melanoma caseswill rise by 12%.
- Norway, Denmark and the Netherlands had the highest rates in 2018.
The American Cancer Societys estimates that around 97,000 cases of melanoma will be diagnosed in 2019
- At 12.7 cases per 100,000 people, the rate of melanomas in the US was less than half of that in Australia at 33.6.
- It is estimated that 81.7% of melanoma cases in 2012 in Europe were attributable to ultraviolet radiation.
- We are exposed to UV light either from the sun or other sources such as tanning devices.
Minimising our exposure to UV light, for example by wearing a high factor sun protection factor , can help to reduce the risk of developing all skin cancers including melanoma.
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer has concluded that those who use tanning beds before the age of thirty may be as much as 75% more likely to develop malignant melanoma.
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
How Skinvision Can Help You
SkinVision enables you to check your skin spots for signs of skin cancer within 30 seconds. Our algorithm is currently at the level of a specialist dermatologist.In skin spots with a potential health risk, SkinVision provides feedback about the preferred next step to take.
SkinVision also enables you to store photos to keep track of changes over time, helping you to monitor your health in the long term.
The efficient and easy-to-use solution is available for iOS and Android and helps to make skin monitoring a simple routine.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are by far the most common skin cancers, and actually are more common than any other form of cancer. Because they rarely spread to other parts of the body, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are usually less concerning and are treated differently from melanoma. These cancers are discussed in Basal and Squamous Cell Skin Cancer.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented
Skin cancer is almost entirely preventable. Making a part of your life, avoiding sunburn, and checking your skin regularly will help prevent further damage to your skin.
Protect your skin from UV radiation and help prevent skin cancer by:
- slipping on sun-protective clothing: cover your shoulders, neck, arms, legs and body.
- slopping on sunscreen thats rated SPF 30+ or higher, broad-spectrum and water resistant.
- slapping on a hat that shades your face, neck and ears.
- seeking shade under trees, umbrellas and buildings from direct sunlight and reflective surfaces.
- sliding on sunglasses that wrap around your face to protect your eyes and surrounding skin.
- staying away from sun lamps, solariums or sunbeds, which emit dangerous levels of UV radiation.
UV radiation from the sun varies depending on time of day, season, where you live and cloud coverage. Protect your skin whenever UV Index levels are above 3. Use Cancer Council Australias free SunSmart app to check the UV Index for your area any time.
Most Australians will get enough vitamin D even with sun protection at UV level 3 or above. Babies and children should be protected from the sun, since they are particularly vulnerable to UV radiation harm.
While using fake tanning cream isnt harmful to your skin, it offers no protection from UV radiation. You still need to protect yourself from the sun.
What Is Skin Cancer And Melanoma
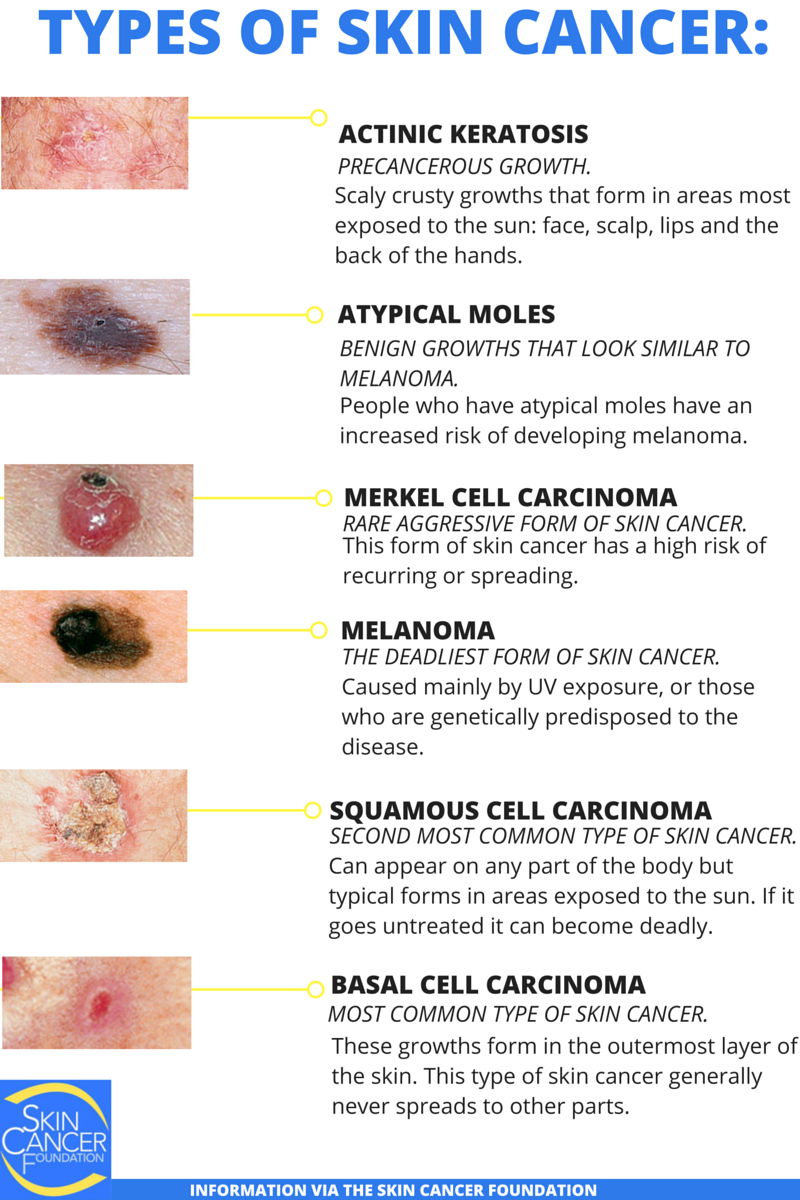
Skin cancer is a disease that occurs when your skin cells grow abnormally, usually from too much exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
This uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells forms a tumour in the skin. Tumours are either benign , or malignant .
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer: each year, more than 13,000 Australians are diagnosed with a melanoma and almost 980,000 new cases of non-melanoma skin cancers are treated. Skin cancer is mostly preventable, and there are effective treatment options available.
Skin cancers are named according to the cells in which they form. There are 3 main types:
- Basal cell carcinoma begins in the lower segment of cells of the epidermis your outer layer of skin. These tend to grow slowly, and rarely spread to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma grows from the flat cells found in the top layer of your epidermis. SCC can grow quickly on the skin over several weeks or months. Bowens disease is an early form of SCC that hasnt grown beyond the top layer of skin.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes cells that give your skin its colour. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer but is considered the most serious because it can spread quickly throughout the body.
BCC and SCC are also called non-melanoma skin cancers. BCC represents more than 2 in 3 non-melanoma skin cancers, and around 1 in 3 are SCC. There are other types of non-melanoma skin cancers, but they are rare.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival
What Is A Melanocyte
Melanocytes are skin cells found in the upper layer of skin. They produce a pigment known as melanin, which gives skin its color. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. When skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, it causes skin damage that triggers the melanocytes to produce more melanin, but only the eumelanin pigment attempts to protect the skin by causing the skin to darken or tan. Melanoma occurs when DNA damage from burning or tanning due to UV radiation triggers changes in the melanocytes, resulting in uncontrolled cellular growth.
About Melanin
Naturally darker-skinned people have more eumelanin and naturally fair-skinned people have more pheomelanin. While eumelanin has the ability to protect the skin from sun damage, pheomelanin does not. Thats why people with darker skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma than fair-skinned people who, due to lack of eumelanin, are more susceptible to sun damage, burning and skin cancer.
When Should I Apply Sunscreen
Every day! The best practice is to apply 30 minutes before venturing outside to allow the sunscreen to bind to your skin. Reapply every two hours of exposure and immediately after swimming or excessive sweating.
Even when its cloudy, up to 80 percent of the suns UV radiation reaches the earth. Going unprotected on an overcast day can lead to skin damage.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Other Cancers And Pre
Actinic Keratosis is a common pre-cancerous growth that may develop into squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated. This growth appears as a rough, scaly patch on your skin that may be pink-red or flesh colored and develops from years of exposure to the sun. Its most commonly found on the face, lips, ears, back of the hands, forearms, scalp, or neck.
Keratoacanthoma is a low-grade, slow growing and typically benigntumor that looks like a tiny dome or crater. Keratoacanthoma originates in the skins hair follicles and often goes away on its own. KA is considered by some to be a highly differentiated form of squamous cell carcinoma.
Kaposi Sarcoma KS is not a skin cancer but a cancer that can appear on the skin or on mucosal surfaces. The lesions or tumors are often brownish-red to purple or blue in color and usually found on the legs, feet and face. This cancer is caused by a type of herpes virus, typically in patients with weakened immune systems, such as those with AIDS.
Lymphoma of the Skin, or Cutaneous Lymphoma, is a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that can appear as a rash or bumps on the skin. Most cases of lymphoma form in the lymph nodes, but lymphomas may also develop in other lymphoid tissue, including the spleen, bone marrow, and skin.
Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
The most common sign of melanoma is the appearance of a new mole or a change in an existing mole.
This can happen anywhere on the body, but the most commonly affected areas are the back in men and the legs in women.
Melanomas are uncommon in areas that are protected from sun exposure, such as the buttocks and the scalp.
In most cases, melanomas have an irregular shape and are more than 1 colour.
The mole may also be larger than normal and can sometimes be itchy or bleed.
Look out for a mole that gradually changes shape, size or colour.
Superficial spreading melanoma are the most common type of melanoma in the UK.
They’re more common in people with pale skin and freckles, and much less common in people with darker skin.
They initially tend to grow outwards rather than downwards, so they do not pose a problem.
But if they grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin, they can spread to other parts of the body.
You should see a GP if you have a mole that’s getting bigger, particularly if it has an irregular edge.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Why Should I Use Sunscreen
Sunscreen reduces your overall UV exposure and lowers your risk of skin cancer and sun damage.
Other things to consider
- Your skin cancer risk factors: Your skin type and family history will determine the level of protection needed for you.
- : No matter your skin type, certain medications and disorders make your skin highly sensitive to the sun, raising your protection requirements.
- Skin conditions: You can choose from sunscreens for dry skin, oily skin, acne-prone skin and sensitive skin.
Live a sun-safe life
Keep in mind that while crucial, sunscreen alone is not enough. Seek the shade whenever possible, wear sun-safe clothing, a wide-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses, for a complete sun protection strategy.
To help you select sun-safe products, look for the Skin Cancer Foundations Seal of Recommendation and browse our recommended sunscreen products.
Skin Cancer By Race And Ethnicity
Race and ethnicity influence a persons skin tone, which affects the appearance of skin cancer. In lighter skin tones, skin cancer may be red, brown, or black. In deeper skin tones, it may be a similar color to the surrounding skin or darker.
White people are more likely to develop many types of skin cancer than any other racial group. This is because they have less melanin in their skin, which gives skin its color. Melanin provides some protection against UV light, which is a leading cause of skin cancer.
However, people of any race or ethnicity can develop skin cancer, and UV exposure may not be the only risk factor at play. It is likely that numerous factors influence a persons risk for developing skin cancer.
In this article, learn more about the differences in skin cancer by race and ethnicity, including survival rates in the United States.
You May Like: Merkel Cancer Prognosis